In the pursuit of a healthy and fulfilling life, the role of food cannot be overstated. Beyond mere sustenance, food has the power to nourish our bodies, uplift our spirits, and even aid in the healing process. The relationship between diet and wellbeing has been recognized for centuries, and modern science continues to uncover the intricate connections between what we eat and how we feel. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of the healing power of food and the impact it can have on our overall wellbeing.
Food as Medicine: Ancient Wisdom and Modern Science
The idea of “food as medicine” dates back to ancient civilizations, where traditional healing systems like Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese Medicine emphasized the importance of using food to maintain health and treat ailments. These ancient practices recognized that certain foods possess healing properties that can support the body’s natural ability to heal itself.
In recent decades, scientific research has shed light on the mechanisms behind the healing power of food. Nutritional science has revealed the presence of essential nutrients, antioxidants, and bioactive compounds in various foods that play vital roles in supporting bodily functions, strengthening the immune system, and reducing inflammation.

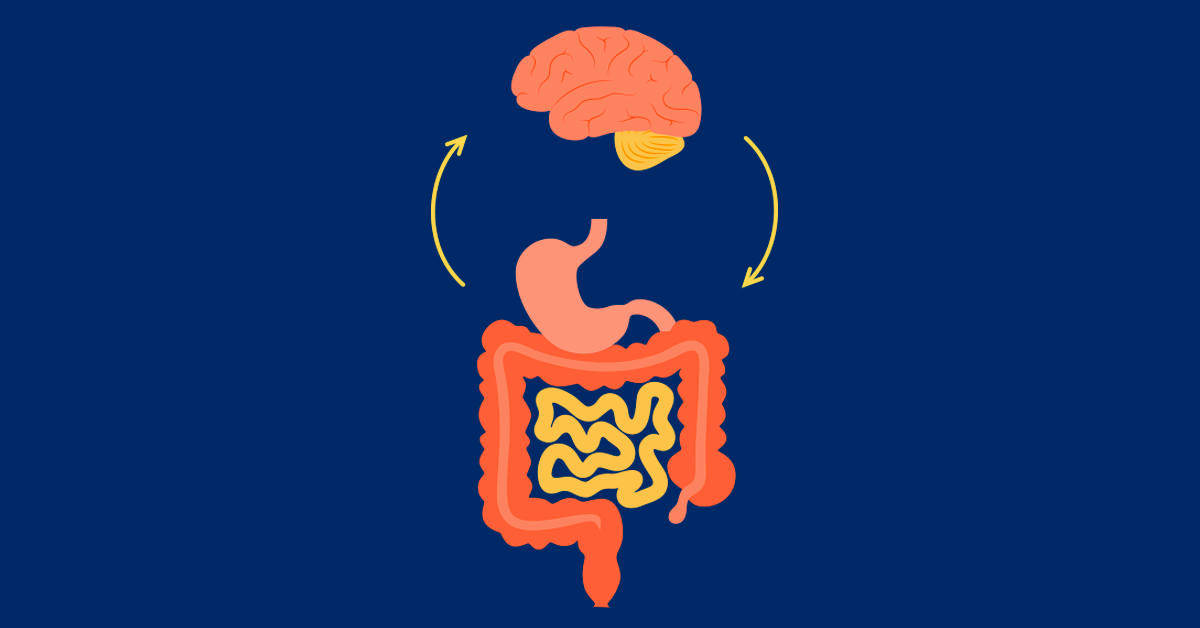
The Gut-Brain Connection
One of the most intriguing discoveries in modern research is the intimate connection between the gut and the brain, known as the gut-brain axis. The gut is home to trillions of microbes, collectively known as the gut microbiota, which play a crucial role in digestion and overall health.
Emerging evidence suggests that the gut microbiota can influence brain function, mood, and behavior through the production of neurotransmitters and other signaling molecules. The foods we eat have a profound impact on the composition and diversity of our gut microbiota, highlighting the importance of a balanced and varied diet for mental wellbeing. We will introduce you to Culinary Festivals around the world, more details at this link.
Eating for Mental Health
The standard Western diet, high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats, has been linked to an increased risk of mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety. Conversely, diets rich in whole foods, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats have been associated with better mental health outcomes.
Specific nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish, nuts, and seeds, have been shown to support brain health and reduce the risk of depression. Foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries, dark leafy greens, and cocoa, can help combat oxidative stress and inflammation, which are implicated in various mental health conditions.
The Role of Food in Chronic Disease Management
Chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and obesity are major global health challenges. While genetics and lifestyle factors contribute to these conditions, diet plays a fundamental role in their prevention and management.
The Mediterranean diet, characterized by abundant fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and olive oil, has been extensively studied for its positive impact on heart health and longevity. This diet is rich in antioxidants, healthy fats, and fiber, which can help reduce inflammation and support cardiovascular function.
For individuals with diabetes, adopting a low-glycemic diet, which focuses on foods that do not cause rapid spikes in blood sugar, can aid in blood glucose control and reduce the risk of complications.
The Canadian Guidelines for Healthy Eating
In Canada, the government promotes healthy eating through the Canadian Guidelines for Healthy Eating, which offer evidence-based recommendations for a balanced and nutritious diet. These guidelines emphasize the consumption of a variety of vegetables and fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, while limiting processed foods, added sugars, and sodium. (Source: Government of Canada – Canada’s Food Guide)
Addressing Food Insecurity
Access to nutritious food is a fundamental human right, yet many people around the world face food insecurity. In Canada, organizations like Food Banks Canada work tirelessly to alleviate hunger and provide support to vulnerable communities.
The Mindful Eating Approach

In addition to the nutritional aspect, the way we eat also influences our wellbeing. Mindful eating is a practice that encourages us to be present and fully engaged during meals, paying attention to the taste, texture, and aroma of food. This approach fosters a healthy relationship with food, helping to prevent overeating and emotional eating.
Culinary Therapy: Food for the Soul
Beyond its physical and mental benefits, food can also nourish the soul. Culinary therapy is an emerging field that explores the therapeutic effects of cooking and sharing meals. Engaging in the process of preparing a meal can be a meditative and creative experience, promoting relaxation and stress reduction.
Furthermore, sharing meals with loved ones fosters social connections and a sense of community, which are vital aspects of overall wellbeing.
In Conclusion: A Recipe for Wellbeing
The healing power of food extends beyond taste and nutrition; it encompasses physical, mental, and emotional wellbeing. Embracing a diet rich in whole, nutrient-dense foods and adopting mindful eating practices can pave the way to a healthier and more fulfilling life.
As we continue to unravel the mysteries of the intricate relationship between diet and wellbeing, one thing remains clear: food is not just fuel; it is a source of nourishment, healing, and joy, making each meal an opportunity to savor the flavors of life.